What is an exosome?
Exosomes are tiny vesicles, approximately 1/1000th the size of a cell and 30-150 nanometers in diameter, secreted by cells. They contain genetic information, growth factors, and proteins and have a lipid membrane. Exosomes are vesicles secreted from stem cells, but they are not cells themselves. Their main function is to facilitate intercellular communication. These vesicles carry proteins, lipids, RNA, and other biomolecules.
Exosomes are not found in food and therefore cannot be obtained through diet. They are produced by body cells. However, a healthy and balanced diet allows cells to function properly, increasing exosome production.
How are exosomes obtained?
Exosomes used for therapeutic purposes are produced in laboratories with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) conditions approved by the Ministry of Health and undergo 10 different quality and characterization tests. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells are multiplied using appropriate culture methods, and when they reach sufficient numbers, they are made to produce exosomes. The resulting exosomes are purified using purification methods and stored as a homogeneous suspension in a sterile cold chain.
Exosomes are evaluated in a variety of medical and scientific fields, including:
Dermatology: Skin rejuvenation, anti-aging approaches, scar appearance, pigmentation issues, hair thinning, collagen
support, burns, atopic dermatitis, eczema
Cardiology: Post–myocardial infarction tissue support and angiogenesis research
Orthopedics: Cartilage health, joint conditions, inflammation-related studies
Oncology: Investigated as drug-delivery systems for targeted therapy
Neurology: Studies involving Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke-related tissue repair
Sources of Exosomes
Exosomes may be obtained from human donors, animal sources, or plant-derived systems.
What Are Exosomes Used For?
Exosomes can be applied in dermatology and aesthetic medicine to support various conditions related to the skin and scalp: Skin Rejuvenation and Anti-Aging Support Exosomes may contribute to improved skin texture, tone, and the stimulation of collagen production. Scar and Wound Management Due to their role in cell signaling, exosomes may support tissue repair processes and help regulate inflammatory responses. Hair Support Applications Exosomes may help nourish hair follicles and support a healthier scalp environment.
Who Is Not Suitable for Exosome Treatment?
The following individuals may not be suitable candidates:
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals
Those with active infection
Individuals with bleeding disorders
Those with autoimmune diseases
Individuals whose medical condition is not appropriate according to physician evaluation
A medical assessment is required before treatment.
Possible Side Effects
Infection risk in non-sterile conditions
Mild swelling or redness at the injection site
Temporary tenderness or discomfort
Rare allergic reactions
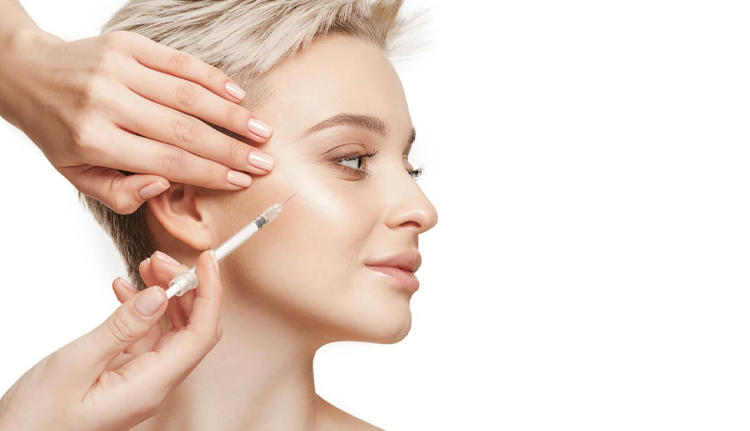


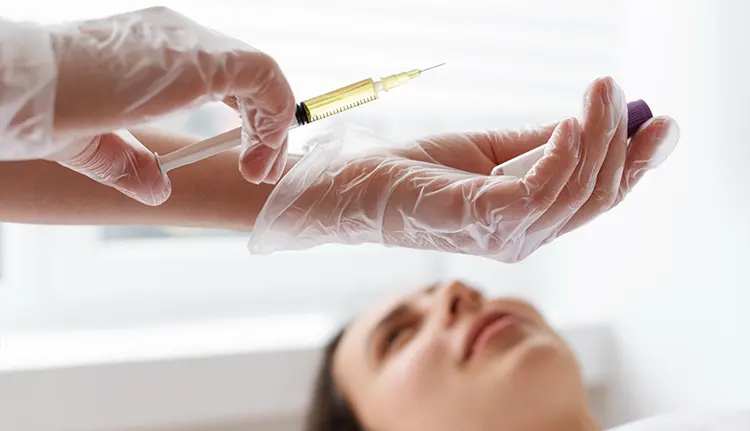
How Is Exosome Therapy Applied?
Exosomes are commonly administered via mesotherapy (micro-needling) techniques to the targeted area.
Topical forms are also used in aesthetic applications, while systemic forms are investigated in other medical fields.
When Do Results Appear?
The effects of exosome treatment may begin to appear within 3–4 months, with tissue renewal continuing for 6–8 months.
Recommended Number of Sessions
Depending on the indication and treatment area, 1–3 sessions may be recommended.
The treatment plan and intervals are determined by the physician.
